A recent report has unveiled a surprising consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, revealing that its effects extended beyond Earth, influencing conditions as far away as the moon.
As the highly contagious virus spread globally, instilling widespread fear and leading to numerous fatalities, countries implemented strict lockdowns, resulting in a drastic reduction in human activity.
While the sight of deserted streets, halted air travel, and paused economic activities was unsettling for many, the lockdowns produced an unintended positive outcome for the environment. Air quality significantly improved as a direct result of the decrease in air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, observable within weeks of the lockdown measures.
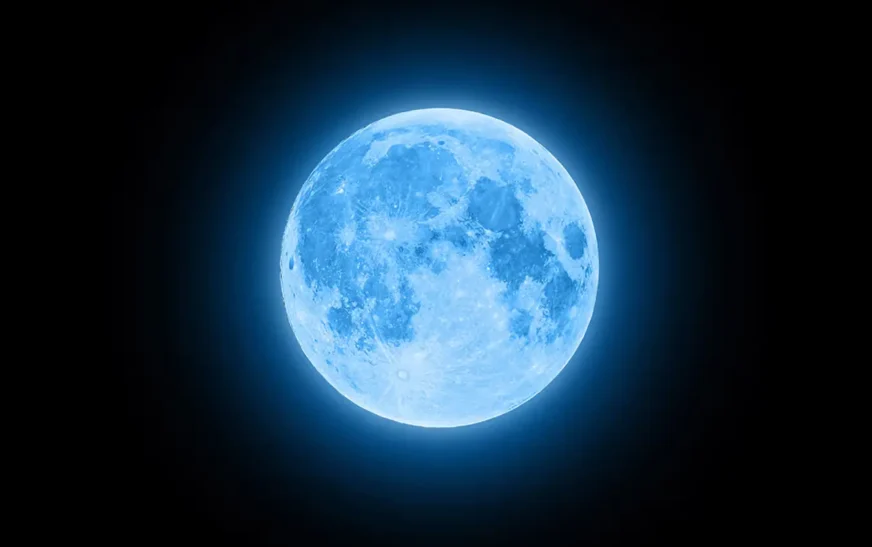
Lunar surface temperatures cooled amidst global lockdowns
New research, conducted by a team from India’s Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) and published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, has indicated that the global COVID-19 lockdowns in 2020 resulted in a notable decrease in lunar surface temperatures.
Read More: Psychologists share effective strategies to prevent online addiction in children
The study revealed that lunar nighttime temperatures experienced a significant dip of approximately 8 to 10 percent Kelvin per month during the April-May 2020 lockdown period compared to the same timeframe in previous years.
Led by researchers K Durga Prasad and G Ambily, the team analyzed data from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, focusing on six different sites on the moon’s nearside from 2017 to 2023.
The findings suggested that fewer greenhouse gas emissions and aerosols during the lockdown led to less heat being trapped and re-emitted by Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to the cooler lunar conditions.
The study reported an anomalous drop in lunar night-time surface temperatures across all sites during the strict global lockdown, with the lowest recorded temperature in 2020 at 96.2 Kelvin.
In contrast, the highest recorded lowest temperature at another site in 2022 was 143.8 Kelvin. The authors noted a noticeable trend of colder temperatures in 2020, with conditions beginning to return to previous levels as human activity resumed in 2021 and 2022.
While the authors acknowledge that more data is needed to definitively link Earth’s radiation changes to lunar surface temperatures, they suggest that future moon-based observatories could play a crucial role in studying Earth’s climate and environmental shifts.
This discovery underscores the interconnectedness of Earth with its celestial neighbor, offering new insights into the broader cosmic impacts of human activities.